Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Trump’s pivot toward welcoming more Chinese students signals a *shift from security-first to revenue-first* thinking.
- Streamlined visa processing already shows higher approval rates and faster turnaround times.
- A rebound in Chinese enrolment could inject **over £12 billion** annually into the U.S. economy.
- Universities are expanding Mandarin-language services to *smooth integration* and boost retention.
- The strategy doubles as *soft-power diplomacy*, potentially easing broader U.S.–China tensions.
Table of Contents
Background on Policy Shift
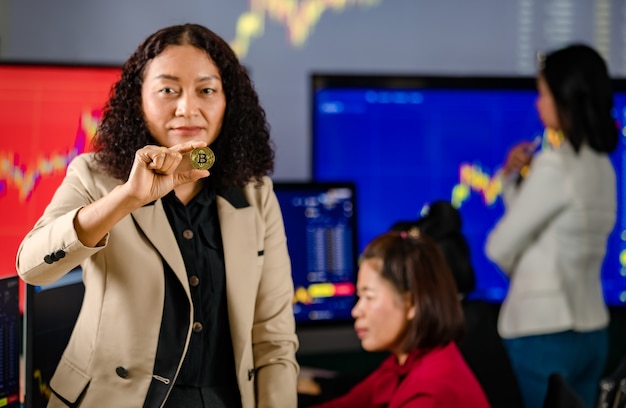
For most of his tenure, Donald Trump’s *“America First”* stance imposed strict limits on study visas, particularly for Chinese nationals viewed through a security lens. Enhanced checks and shorter visa durations throttled thousands of applications, prompting university leaders to warn of lost fees and weakened research capacity. Their lobbying, supported by data from the Institute of International Education, appears to have nudged the administration toward a more pragmatic, revenue-oriented approach.
“When budgets meet ideology, budgets usually win,” quipped one Ivy League provost, underscoring how economic realities have eclipsed earlier espionage fears.
Visa Policy & Processing
The F-1 study visa and J-1 exchange visa just received procedural upgrades for Chinese nationals: shorter paperwork, clearer documentation lists, and separate queues at U.S. consulates. According to the U.S. Department of State, average processing times dropped from ten weeks to four, while approval rates climbed by roughly 9 percentage points.
- Consular staff now route bona fide study cases away from broader immigration backlogs.
- Security vetting remains intact but is initiated earlier to avoid last-minute denials.
- Universities receive real-time status updates, helping them plan orientation and housing.
Impact on Admissions
Early data from flagship state systems show a 15 % uptick in Chinese applications for Fall 2025. Engineering, business, and computer science remain the top draws. To convert offers into enrolments, campuses are hiring Mandarin-speaking advisers and launching targeted mental-health programs.
Joint-degree agreements with mainland institutions, tracked by the NAFSA Association, have risen 22 % year-on-year, suggesting deeper academic integration on the horizon.
Economic Implications
A single Chinese student spends between £45,000 and £85,000 annually on tuition, housing, and living costs. Nationally, their contribution tops **£12 billion**, sustaining jobs in housing, retail, and campus services. Because many pay full fees, they effectively *cross-subsidise* laboratory upgrades and domestic scholarships.
University towns from Ames, Iowa to Gainesville, Florida report rent and dining rebounds that trace directly to the renewed Chinese presence.
Political Considerations
Welcoming more Chinese students doubles as *soft-power diplomacy*. Graduates who return home carry first-hand experience of U.S. life, a factor researchers at the Center for Security and Emerging Technology describe as “invaluable diplomatic capital.” Domestically, the policy helps American universities fend off competition from the UK, Canada, and Australia, all of which aggressively court Chinese applicants.
Educational Benefits & Challenges
Chinese scholars excel in STEM labs, often accelerating publication timelines and broadening classroom debate. Their presence pushes institutions to refine support systems—writing centres, language exchanges, and cross-cultural workshops that benefit *all* students.
Integration remains the main hurdle. Universities are therefore boosting peer-mentoring schemes and career advising tailored to international cohorts.
Trump Initiatives
New White House directives instruct consular posts to treat genuine study applicants as a *priority group*. Meanwhile, universities receive clearer compliance guidelines, making recruitment trips to Beijing and Shanghai less risky. Cooperative research grants now face fewer regulatory barriers, allowing both countries to tap each other’s academic strengths without diluting security safeguards.
Future Outlook
Rising incomes and fierce competition for coveted Chinese university seats will keep demand for U.S. degrees strong. If Washington maintains streamlined visas and robust campus support, enrolment could return to pre-restriction peaks within three admission cycles.
Yet, as one admissions dean put it, *“The tap can turn off as quickly as it was opened.”* Escalating geopolitical tension could re-tighten visa rules overnight, so universities are hedging bets with dual-degree pathways and diversified recruitment beyond East Asia.
FAQ
Why did Trump change course on Chinese student visas?
Economic data showing multi-billion-pound benefits—and lobbying from cash-strapped universities— outweighed earlier security concerns.
Are security checks being relaxed?
No. *Selectivity remains*, but background screening now starts earlier, preventing last-minute denials and long delays.
How quickly could enrolment rebound?
Analysts expect a full rebound within three admission cycles—assuming the streamlined visa process holds.
Which majors attract the most Chinese students?
Engineering, business, computer science, and increasingly data analytics remain the top choices.
Could the policy reverse again?
Yes. A spike in U.S.–China tensions could prompt renewed restrictions, so universities are diversifying their international recruitment strategies.